Cybersecurity researchers found two harmful packages in the Python Package Index, or PyPI, repository. These packages, sisaws and secmeasure, were created to install a remote access trojan named SilentSync on Windows computers.
According to researchers at Zscaler ThreatLabz, SilentSync can execute commands remotely, steal files, and capture screenshots. It also takes data from web browsers such as Chrome, Brave, Edge, and Firefox, including credentials, browsing history, autofill information, and cookies.
The two packages, which have now been removed from PyPI, were uploaded by a user named “CondeTGAPIS.” The package sisaws was downloaded 200 times, while secmeasure had 627 downloads.
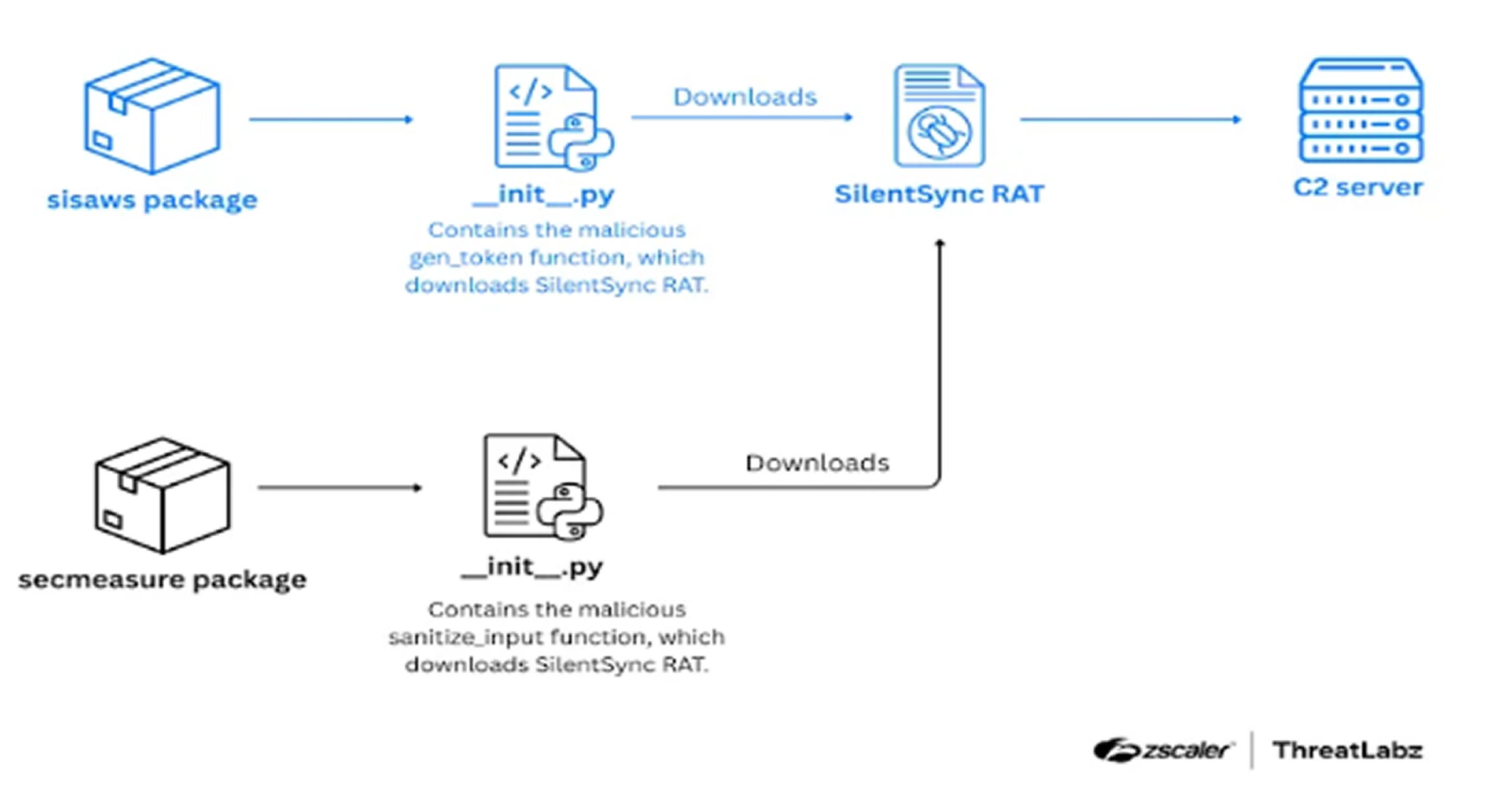
Zscaler noted that sisaws mimics the legitimate Python package sisa, which is part of Argentina’s national health system. The malicious version contains a function called gen_token() that downloads the next stage of the malware. This function sends a specific token and receives a second token in response, similar to the real SISA API.
If a developer imports the sisaws package and uses the gen_token function, the code decodes a hexadecimal string. This string reveals a command that is used to download an additional Python script. This script is saved as helper.py in a temporary folder and then executed.
Similarly, secmeasure pretends to be a library for cleaning strings and applying security measures, but it also installs the SilentSync trojan. While SilentSync primarily targets Windows systems, it also has features for Linux and macOS. It makes changes to the Windows Registry, modifies the crontab file on Linux to run on startup, and registers a LaunchAgent on macOS.
The malware uses the second token to make an HTTP GET request to a specific server. The server then sends back Python code that is executed directly in memory. The server has four different endpoints:
- /checkin, to confirm connectivity
- /comando, to request commands to execute
- /respuesta, to send a status message
- /archivo, to send command output or stolen data
The malware can steal browser data, run shell commands, take screenshots, and steal files. It can also zip up and steal entire directories. After the data is sent, all the malicious files are deleted from the computer to avoid detection.
Zscaler stated that the discovery of sisaws and secmeasure shows the growing threat of supply chain attacks in public software repositories. By using techniques like typosquatting and impersonating legitimate packages, attackers can gain access to personal information.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



