A massive phishing campaign is actively targeting travelers worldwide, utilizing over 4,300 fake domains to steal payment card information. This sophisticated operation focuses on individuals planning vacations or about to check into hotels by sending convincing, fake booking confirmation emails that appear to originate from trusted travel companies.
The Phishing Operation
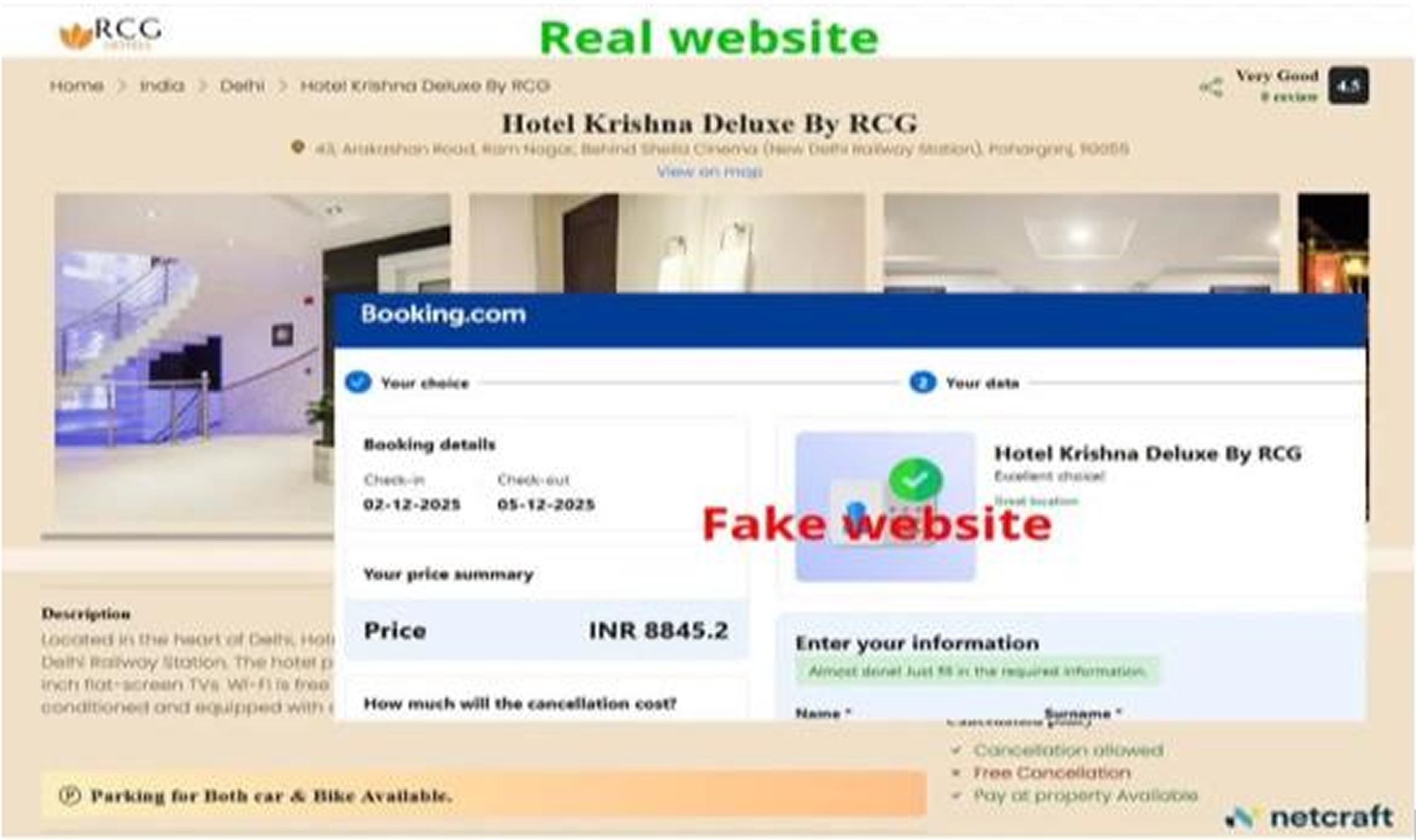
Attackers created a vast network of scam websites that mimic real hotel reservation pages, complete with professional layouts and familiar logos, making them highly deceptive. The
campaign uses a well built phishing kit that manages a complex redirection chain. When a victim clicks a link in the fake email, their browser is redirected through several intermediate websites before landing on the actual phishing page.
The emails create a sense of urgency, claiming that a hotel reservation must be confirmed within 24 hours to avoid cancellation, pushing victims to act quickly without scrutinizing the details. The fake pages mimic major travel brands, including Airbnb, Booking.com, Expedia, and Agoda, using their exact logos and design.
Technical Sophistication
Security researchers at Netcraft identified the threat actor as Russian speaking, based on extensive Russian language comments found in the phishing kit’s source code. The operation started in February 2025 and has grown rapidly, with the attacker registering new domains almost daily, following predictable patterns with phrases like "confirmation," "booking," and "reservation."
The attack uses a complex, multi step redirection chain to evade security systems. The link first sends the victim to an old, unused domain, then redirects to a page on Google's legitimate Blogspot platform, which finally redirects to the phishing page. This method helps the attackers avoid direct detection and adds a false layer of trust.
Once on the phishing page, victims see a fake Cloudflare CAPTCHA designed to build false confidence before they are asked to enter sensitive information, including their full payment card details. The page attempts a fraudulent transaction in the background while displaying a fake support chat window that tells victims to confirm SMS notifications, which are actually the real fraud alerts triggered by the unauthorized charges. The phishing kit is highly sophisticated, supporting 43 different languages and using a unique identifier in the URL to run multiple campaigns simultaneously, impersonating different brands with customized pages for each victim.
Found this article interesting? Follow us on X(Twitter) ,Threads and FaceBook to read more exclusive content we post.



